Explain How Different Classes of Levers Affect Muscle Efficiency
Such a muscle is triangular or fan shaped like the pectoralis major muscle of the anterior. First class second class and third class.

10 The Muscular System Ppt Download Muscular System Muscles Of Facial Expression Thoracic Cage
Any force applied to the lever is called the effort.
. The general term used for these kinds of muscles is sphincter. Consider an individual who needs surgery to reattach his. In a first-class lever the effort is applied at one end of the lever and the load is at the other with the fulcrum somewhere between.
A first-class lever a second-class lever a third-class lever All lever systems have the same efficiency. Explain how the name of a muscle can help identify its location appearance or. Depending on the relative position of the three elements effort fulcrum and load a lever belongs to one of three classes.
Name the major muscles of the torso and provide a. First- and second-class levers generally are very efficient especially when the loads are located close to the fulcrum while efforts are further from the fulcrum Figures A and C. Position Direction Fascicles arrangement Structural characteristics Action.
Mechanical Advantage is the efficiency of the lever system MAEARA 1st Class Lever fulcrum is located between the applied force and the load. The efficiency of a lever relies on the ratio of the. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area.
They are broken into three classes. Classes of Levers. Fascicle arrangement is correlated to the force generated by a muscle and affects the muscles range of motion.
Start studying Chapter 10 Describe the arrangement of fasciles in the various types of muscles explain the resulting functional differences and explain how different classes and levers affect muscle efficiently. Describe the arrangement of fascicles in the various types of muscles explain the resulting functional differences and explain how different classes of levers affect muscle efficiency. Explain how the name of a muscle can help identify its location appearance or function.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with. The action of a muscle pulling on a bone often works like a type of simple machine called a lever. Its order is represented as force-fulcrum-weight.
When a group of muscle fibers is bundled as a unit within the whole muscle it is called a fascicle. A lever is a rigid rod able to rotate about a fixed point known as a fulcrum formed by the joint. Who are the experts.
Parallel muscles contract about 30 in length. Levers are typically labeled as first class second class or third class. Pennate 4circular Most skeletal muscles are parallel muscles.
11-3 Predict the actions of a muscle on the basis of its origin and insertion and explain how muscles interact to produce or oppose movements. The relatively immovable point of attachment for a muscle. Name the major muscles of the face and provide a function for each as they pertain to facial expression.
See the chart below to visualize the difference between the levers. A muscle fascicle is a group of muscle fibers or cells that are bound together by a membrane of connective tissue called perimysium. Describe the arrangement of fascicles in the various types of muscles explain the resulting functional differences and explain how different classes of levers affect muscle efficiency.
Load between force and pivot. Using scissors represents the. A lever is a system that allows muscles to move a load when they exert enough force by means of fulcrum.
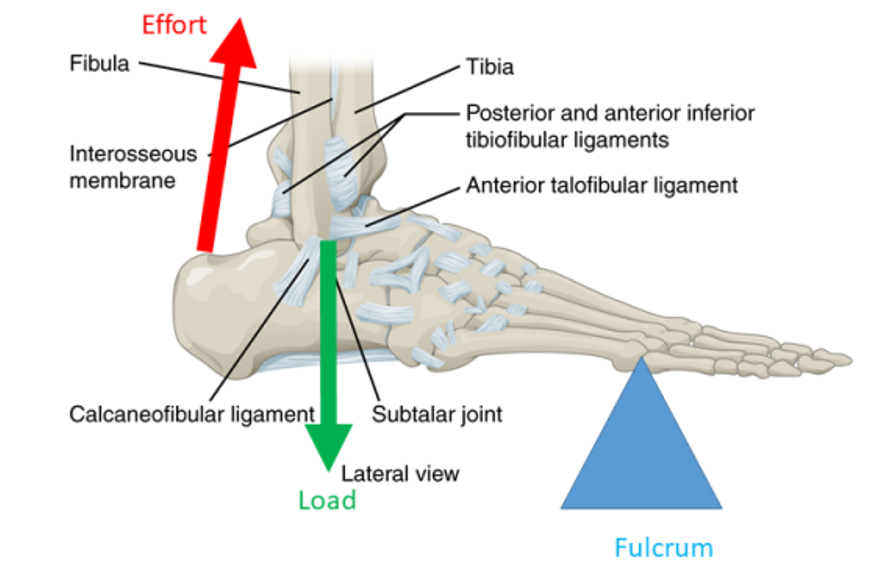
A convergent muscle has a broad origin and its fascicles converge toward a single tendon of insertion. Explain how different classes of levers affect muscle efficiency. Each of these lever classes have unique arrangements of the muscles insertion effort and bones leverarm around the joint fulcrum.
This is the most basic type of lever. Describe the classes of levers and explain how they make muscles more efficient. The 4 patterns of fascicle organization are.
There are three different kinds of levers. Fascicles are covered by a layer of connective tissue called perimysium see Figure 103. The efficiency of first- and second-class levers will decrease when loads move further from the fulcrum Figures B and D.
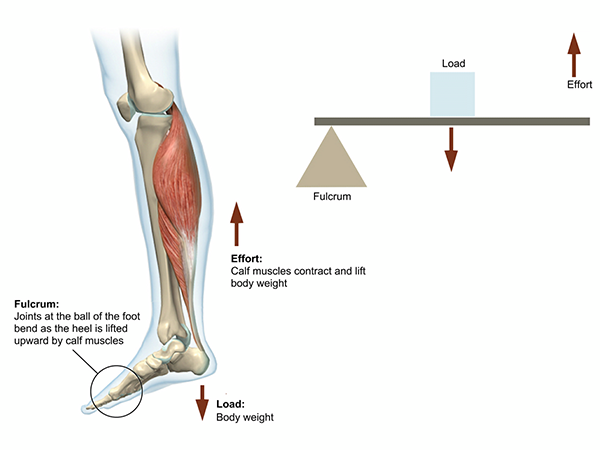
Force and load to either side of the pivot. An example of a first-class lever is a pair of pliers or scissors. Wheelbarrow - the resistance is in the center between the applied force and the fulcrum - a small force can move a large weight Figure 11-2c third-class lever.
The diameter and length of muscle fascicles vary depending on the specific function of the muscle. A first classlever is a lever system like that of the head and shoulders with the joint between the head and vertebrae working as the fulcrum with the fulcrum being in the center. How do the following factors affect hypertrophy atrophy or.
11-4 Explain how the name of a muscle can help identify its location appearance or function. The pivot is the place where your skull meets the top of your spine. Reduces the angle between two body parts.
Their fibers parallel the long axis of the muscle. Identify six different types of descriptive information that can be used to name skeletal muscles. Force between pivot and load.
Explain how the name of a muscle can help identify its location appearance or function. Muscle fascicles bundle muscle fibers together for extra strength allowing the muscle to exert more force. This is a type of lever which has the fulcrum in between the weight and the force applied.
Class 1 lever nod your head. Our hand pushing an object or seesaws crowbars. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
Various types of muscles and explain the resulting functional differences. The movable point of attachment for a muscle. First-class leverage also occurs when you lift your.
All three types are found in the body but most levers in the human body are third class. Seesaw - the fulcrum is in the center between the applied force and the resistance - force and resistance are balanced Figure 11-2b second-class lever. Your skull is the lever arm and the neck muscles at the back of the skull provide the force effort to lift your head up against the weight of the head load.
Biceps brachii When a parallel muscle contracts the center or body of the muscle thickens. Seesaws and scissors are first-class levers. A force that resists the motion of the lever such as the downward force exerted by a weight on.
A lever is an object that can multiply mechanical force effort or resistance force load Lever arm is the distance from the axis of rotation to the line of action of the force. First second and third in order of efficiency. Examples include the orbicularis muscles surround the mouth and eyes.
A first-class lever has the axis fulcrum located between the weight resistance and the force figure 121a. Tension in parallel muscle depends on the total.

Body Levers Body Physics Motion To Metabolism
Comments
Post a Comment